What is Work?
In physics, work done is defined as the product of force applied to an object and its displacement. Work is a scalar quantity and is typically measured in the unit of Joules (J).
Definition
For work to be done, a force must be exerted and there must be motion or displacement in the direction of the force. The work done by a force acting on an object is equal to the magnitude of the force multiplied by the distance moved in the direction of the force. Work has only magnitude and no direction. Hence, work is a scalar quantity.
The formula for work is:
W = F x s
where W is the work done,
F is the force applied
d is the displacement
Work is a measure of the energy transferred to or from an object. When work is done on an object, energy is transferred to the object and the object’s kinetic energy or potential energy increases. When work is done by an object, energy is transferred from the object and the object’s kinetic energy or potential energy decreases.
Here are some simple examples of work:
- Lifting a book from the floor to a table: When you lift a book from the floor to a table, you are applying a force to the book and the book is moving in the direction of the force. As a result, you are doing work on the book.
- Pushing a crate across the floor: When you push a crate across the floor, you are applying a force to the crate and the crate is moving in the direction of the force. As a result, you are doing work on the crate.
- Pulling a sled through the snow: When you pull a sled through the snow, you are applying a force to the sled and the sled is moving in the direction of the force. As a result, you are doing work on the sled.
- Compressing a spring: When you compress a spring, you are applying a force to the spring and the spring is moving in the direction of the force. As a result, you are doing work on the spring.
- Stretching a rubber band: When you stretch a rubber band, you are applying a force to the rubber band and the rubber band is moving in the direction of the force. As a result, you are doing work on the rubber band.
In all of these examples, the work done is positive because the force and the displacement vectors are in the same direction.
Negative work
It is also possible to do negative work. Negative work is done when the force and the displacement vectors are in opposite directions. For example, if you try to lift a book from the floor to a table, but you are unable to do so, you are doing negative work on the book. This is because the force you are applying is
Work and energy
Work and energy are closely related concepts. Energy is the ability to do work. When work is done on an object, its energy increases. When work is done by an object, its energy decreases.
The work-energy principle states that the net work done on an object is equal to the change in the object's kinetic energy. This means that if the net work done on an object is positive, the object's kinetic energy will increase. If the net work done on an object is negative, the object's kinetic energy will decrease.
Applications of work
The concept of work is used in many different fields of physics, engineering, and technology. For example, work is used to calculate the power of an engine, the efficiency of a machine, and the energy required to launch a rocket into space.
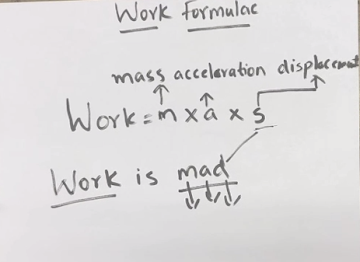
How to memorize Work Formula:
There are many ways to memorize the formula, one such way is by using advanced ACRONYMS method.
Here we have the formula as:
W = m x a x s
Now,
We will make analogies of the words that we have to memorize.
- Work(w)
- Mass(m)
- Acceleration(a)
- Displacement(s) this is represented by ‘s’ but the word start with ‘d’
When we combine it together it forms the sentence:
WORK IS MAD