Momentum
Momentum is a physical quantity that describes how much an object resists changes to its motion. It is calculated by multiplying the mass of an object by its velocity.
In simple words, momentum is mass in motion.
The more mass an object has, the more momentum it has. The faster an object is moving, the more momentum it has.
Momentum is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. The direction of momentum is the same as the direction of the object's velocity.
Momentum is conserved in collisions. This means that the total momentum of a system before a collision is equal to the total momentum of the system after the collision.
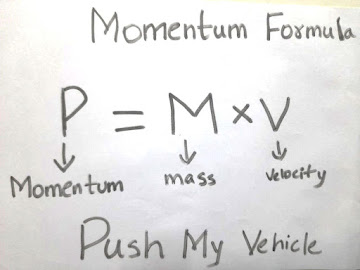
Formula for momentum:
P = M * V
where:
- p is the momentum (in kg m/s)
- m is the mass of the object (in kg)
- v is the velocity of the object (in m/s)
Examples of momentum:
- A bowling ball has more momentum than a baseball, even if they are moving at the same speed. This is because the bowling ball has more mass.
- A car has more momentum than a bicycle, even if they are moving at the same speed. This is because the car has more mass.
- A bullet has a lot of momentum, even though it is very small. This is because it is moving very fast.
Momentum is an important concept in physics and engineering. It is used to understand the motion of objects and to design machines and structures.
Here are some other interesting facts about momentum:
- Momentum is a conserved quantity, which means that it can never be created or destroyed.
- The momentum of a system can be changed by applying a force to the system.
- The force required to change the momentum of an object is proportional to the object's mass and the amount by which its momentum is being changed.
- The direction of the force is always in the opposite direction of the change in momentum.
Momentum is a fascinating concept that has many applications in the real world. It is a key part of our understanding of motion and helps us to design machines and structures that work safely and efficiently.
How to memorize Momentum formula:
Well, there are many ways to memorize formulas, one such way is by using Advanced ACRONYMS concept.
This will help you memorize fast momentum formula for your exam, this will also help you stick this formula in your brain for a longer period time.
It follows a simple concept where it takes out the first letters of the formula that you want to memorize and create analogies with it.
You try to convert the things that you cannot imagine to something which you are able to visualize, you try making a story/sentence out of it.
Here,
The analogies for the formula can be made as
P = M * V
- Momentum (p) = Push
- Mass (m) = my
- Velocity (v) = vehicle
The analogy sentence would be
PUSH MY VEHICLE