JOULE’S LAW OF HEATING
What is Joule's Law
We are aware of the heating impact of electric current. The heat is produced due to the collision electrons in the wire. You might have wondered about the amount of heat generated during the flow of current through a wire and the parameters and conditions it is based upon. To answer all these questions, Joule gave a formula that describes this phenomenon precisely and called it Joule’s Law.
Statement
Joule’s law is a mathematical description of the rate at which resistance in a circuit converts electric energy into heat energy.
History
The English physicist James Prescott discovered that the amount of heat per second that develops in a current-carrying conductor is proportional to the electrical resistance of the wire and the square of the current.
The heat that is generated because of the current flow in an electric wire is described in Joules. The mathematical expression of Joule’s law is as explained below.
Joule’s first law
The joule’s first law shows the relationship between heat produced by flowing electric current through a conductor.
Formula
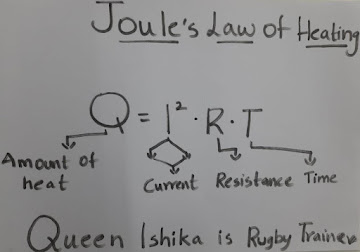
Q = I2 R T
Where,
- Q indicates the amount of heat
- I show electric current
- R is the amount of electric resistance in the conductor
- T denotes time
- The amount of generated heat is proportional to the wire’s electrical resistance when the current in the circuit and the flow of current is not changed.
- The amount of generated heat in a conductor carrying current is proportional to the square of the current flow through the circuit when the electrical resistance and current supply is constant.
- The amount of heat produced because of the current flow is proportional to the time of flow when the resistance and current flow is kept constant.
Here are some examples of Joule's law of heating in action:
- When you turn on a toaster, the current flows through the heating element, which causes the element to heat up and toast your bread.
- When you turn on an electric stove, the current flows through the heating coils, which causes the coils to heat up and cook your food.
- When you turn on a light bulb, the current flows through the filament, which causes the filament to heat up and emit light.
Joule's law of heating can also be used to calculate the amount of heat generated by an electrical device. For example, if you know the current flowing through a toaster, the resistance of the heating element, and the time for which the toaster is turned on, you can use Joule's law to calculate the amount of heat that will be generated.
Joule's law of heating is a simple but important law that is used to explain the operation of many electrical devices. It is also used to calculate the amount of heat generated by electrical devices.
Here are some additional things to keep in mind about Joule's law of heating:
- The heat generated is proportional to the square of the current, which means that if the current doubles, the heat generated will quadruple.
- The heat generated is also proportional to the resistance of the conductor, which means that if the resistance doubles, the heat generated will halve.
- The heat generated is proportional to the time for which the current flows, which means that if the time doubles, the heat generated will double.
Joule's law of heating is a fundamental law of physics that has many applications in the real world. It is used to explain the operation of many electrical devices and to calculate the amount of heat generated by electrical devices.
How to memorize Joule’s Law of Heating:
It can be memorized using many methods, one of the easy methods is by using ACRONYMS advanced method.
It basically takes out the first letters of every word and make another word which is easy to understand as an analogy to it.
In this case we had this formula:
Q = I2 R T
Now,
It should be in such a way that it should form a sentence which sounds weird, funny and easy to visualize.
We allot the things that we want to learn with some analogies
- The amount of heat(Q)= Queen
- Electric Current(I2) = Ishika is
- Resistance(R) = Rugby
- Time (T) = Trainer
If we put this together it forms a sentence such as,
Queen Ishika is Rugby Trainer